Hugging Face Diffusers
🤗 Diffusers is the go-to library for state-of-the-art pre-trained diffusion models for generating images, audio, and even 3D structures of molecules. The W&B integration adds rich, flexible experiment tracking, media visualization, pipeline architecture, and configuration management to interactive centralized dashboards without compromising that ease of use.
Next-level logging in just two lines
Log all the prompts, negative prompts, generated media, and configs associated with your experiment by simply including 2 lines of code. Here are the 2 lines of code to begin logging:
# import the autolog function
from wandb.integration.diffusers import autolog
# call the autolog before calling the pipeline
autolog(init=dict(project="diffusers_logging"))
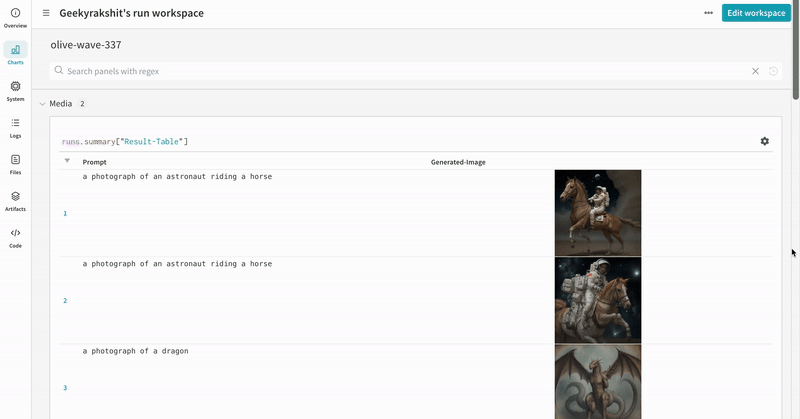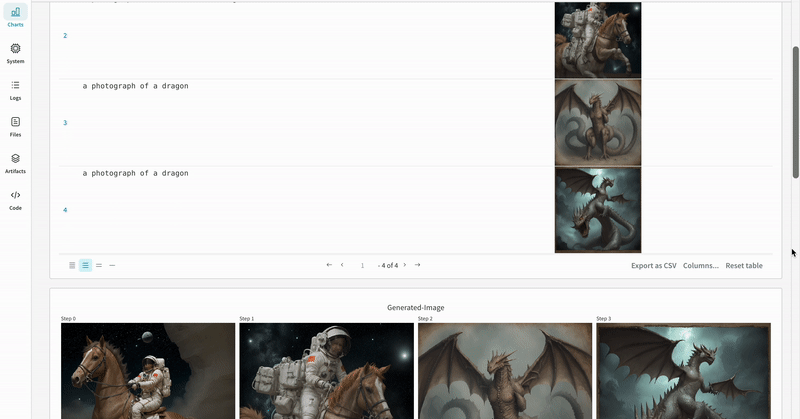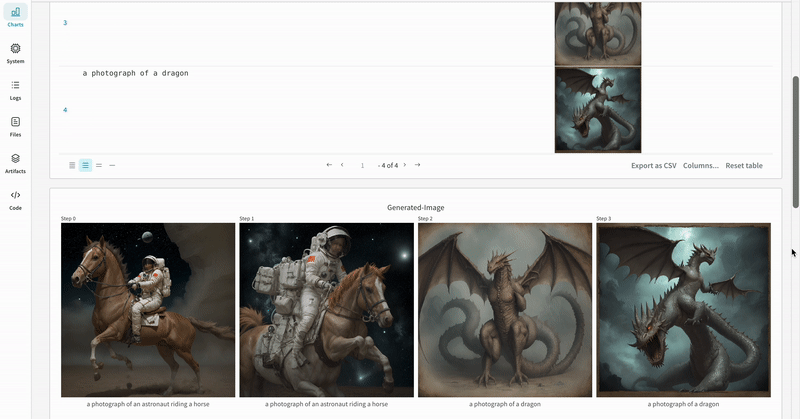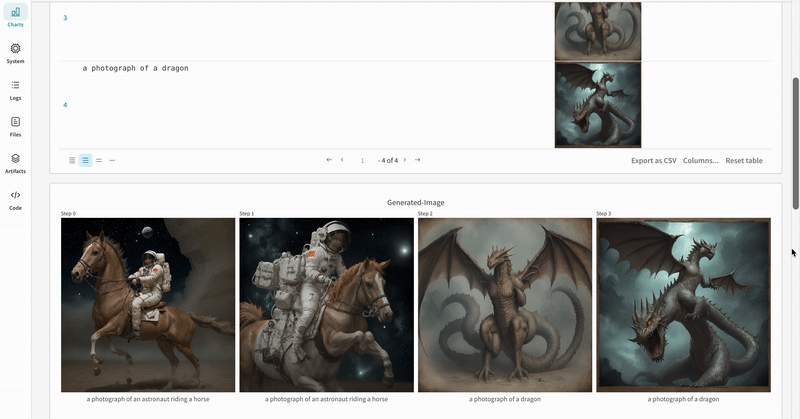 |
|---|
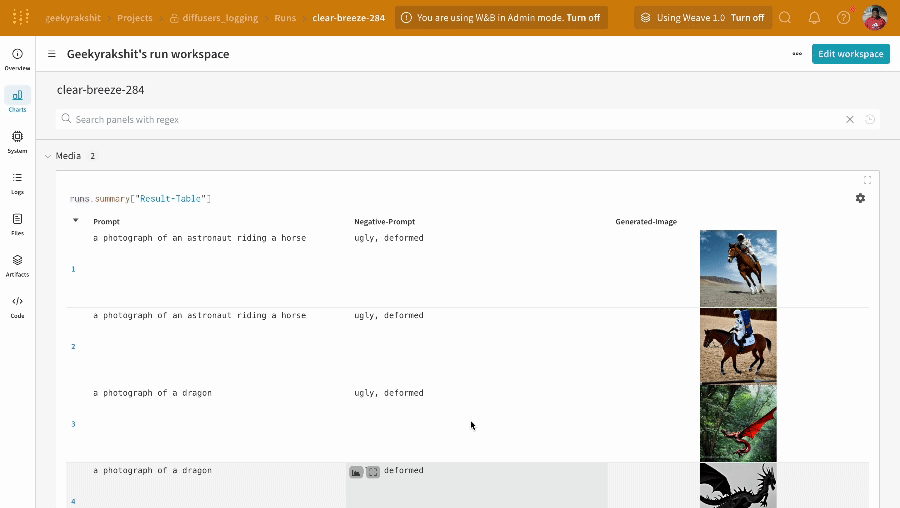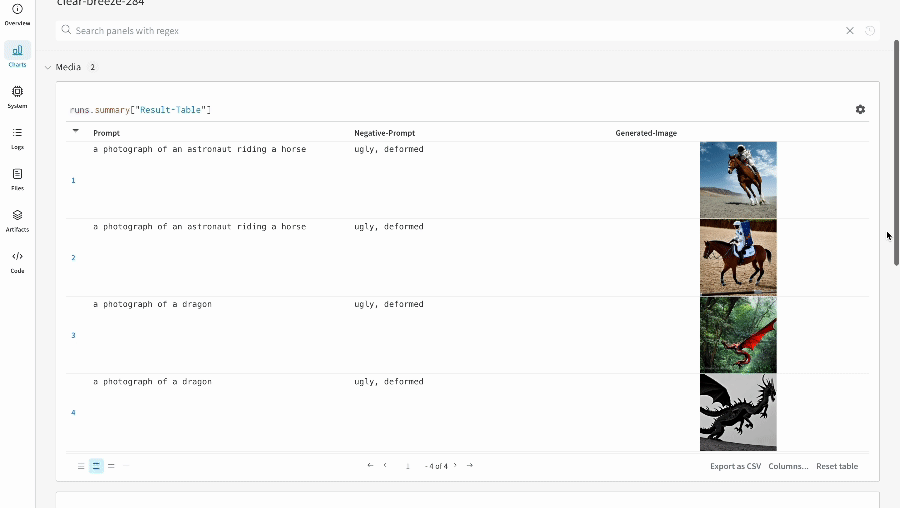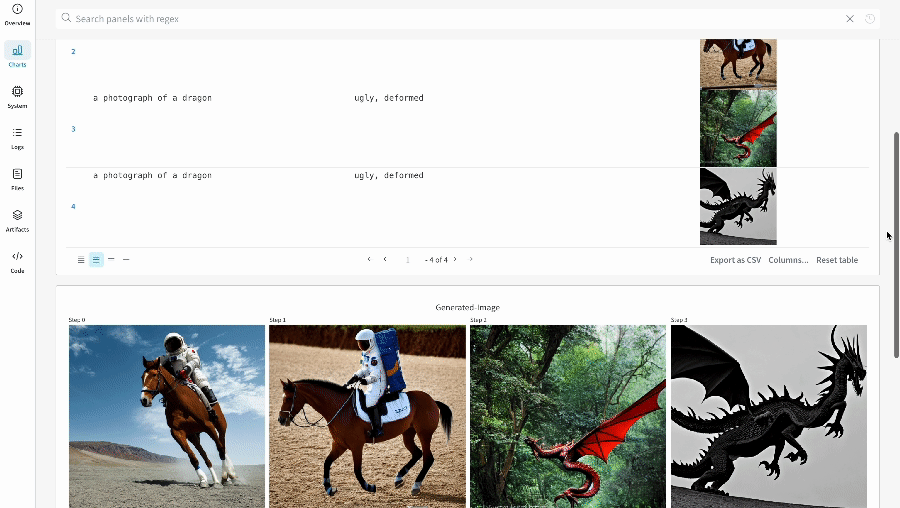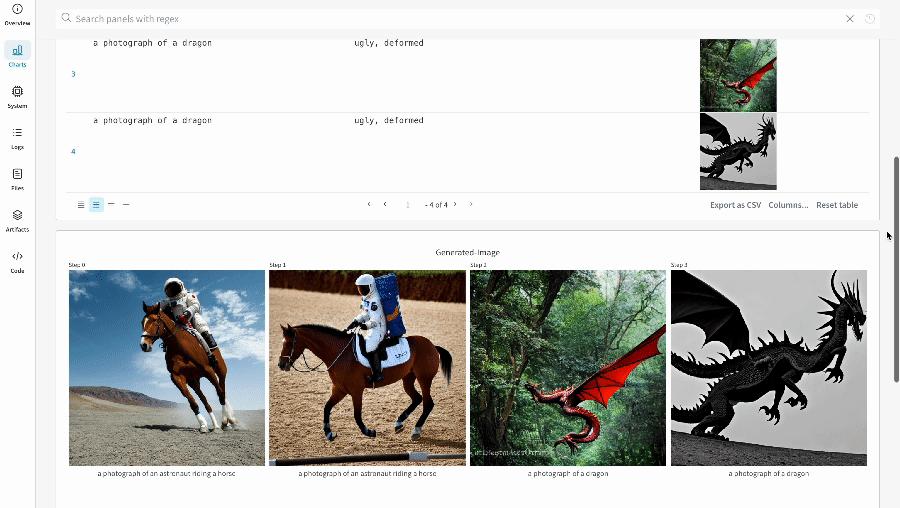
| An example of how the results of your experiment are logged. |
Getting started
First, you need to install diffusers, transformers, accelerate, and wandb.
- Command Line
- Notebook
pip install --upgrade diffusers transformers accelerate wandb
!pip install --upgrade diffusers transformers accelerate wandb
How the autolog works?
The autolog() function can be called with the init parameter which accepts a dictionary of the parameters required by wandb.init().
When autolog() is called, it initializes a Weights & Biases run, which automatically tracks the inputs and the outputs from all supported pipeline calls.
- Each pipeline call is tracked into its own table in the workspace, and the configs associated with the pipeline call is appended to the list of workflows in the configs for that run.
- The prompts, negative prompts, and the generated media are logged in a
wandb.Table. - All other configs associated with the experiment including seed and the pipeline architecture are stored in the config section for the run.
- The generated media for each pipeline call are also logged in media panels in the run.
You can find a list of supported pipeline calls here. In case, you want to request a new feature of this integration or report a bug associated with it, please open an issue on https://github.com/wandb/wandb/issues.
Here is a brief end-to-end example of the autolog in action:
- Python Script
- Notebook
import torch
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
# import the autolog function
from wandb.integration.diffusers import autolog
# call the autolog before calling the pipeline
autolog(init=dict(project="diffusers_logging"))
# Initialize the diffusion pipeline
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16
).to("cuda")
# Define the prompts, negative prompts, and seed.
prompt = [
"a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse",
"a photograph of a dragon"
]
negative_prompt = ["ugly, deformed", "ugly, deformed"]
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(10)
# call the pipeline to generate the images
images = pipeline(
prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
num_images_per_prompt=2,
generator=generator,
)
import torch
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
import wandb
# import the autolog function
from wandb.integration.diffusers import autolog
# call the autolog before calling the pipeline
autolog(init=dict(project="diffusers_logging"))
# Initialize the diffusion pipeline
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1", torch_dtype=torch.float16
).to("cuda")
# Define the prompts, negative prompts, and seed.
prompt = [
"a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse",
"a photograph of a dragon"
]
negative_prompt = ["ugly, deformed", "ugly, deformed"]
generator = torch.Generator(device="cpu").manual_seed(10)
# call the pipeline to generate the images
images = pipeline(
prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
num_images_per_prompt=2,
generator=generator,
)
# Finish the experiment
wandb.finish()
 |
|---|
| An example of how the results of your experiment are logged. |
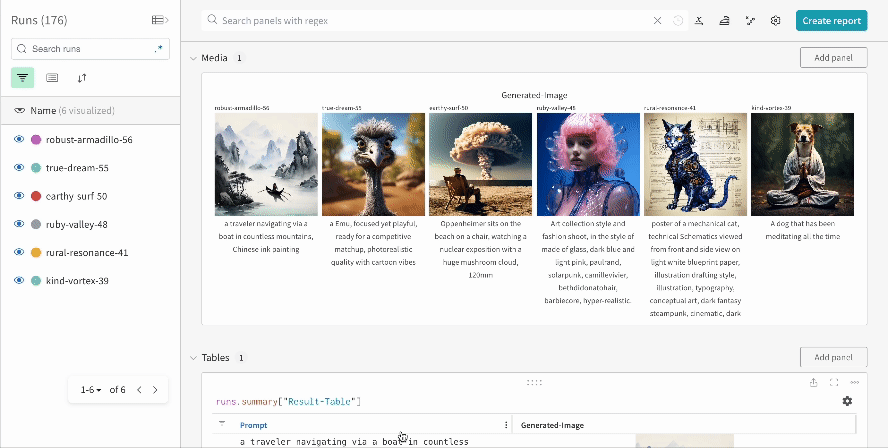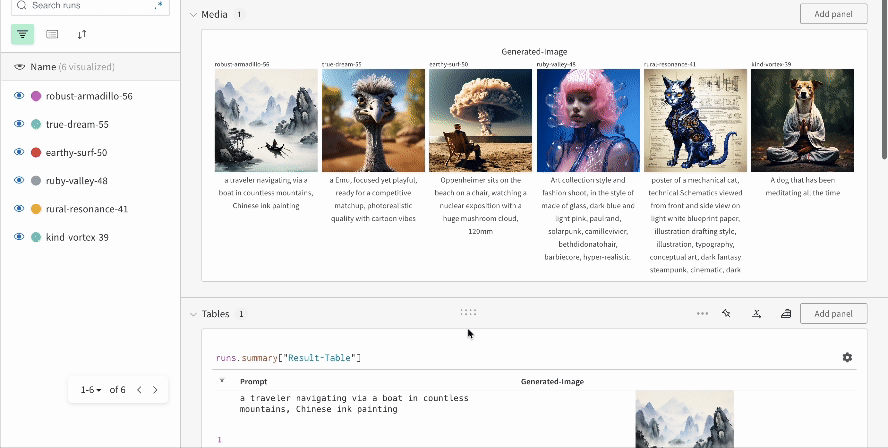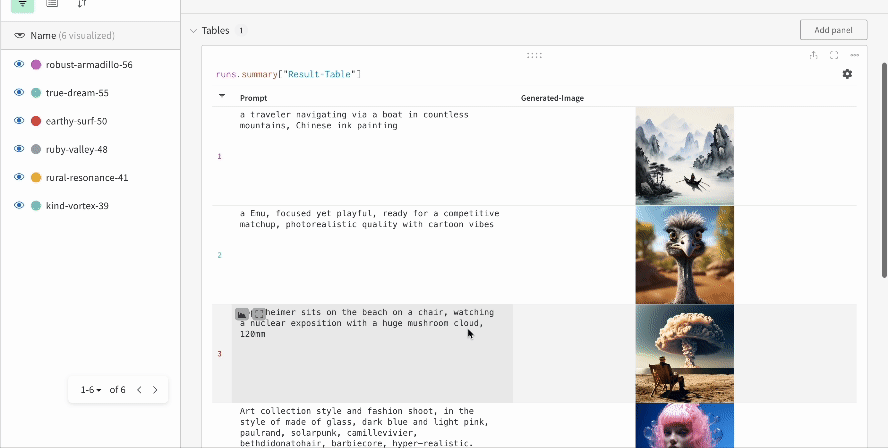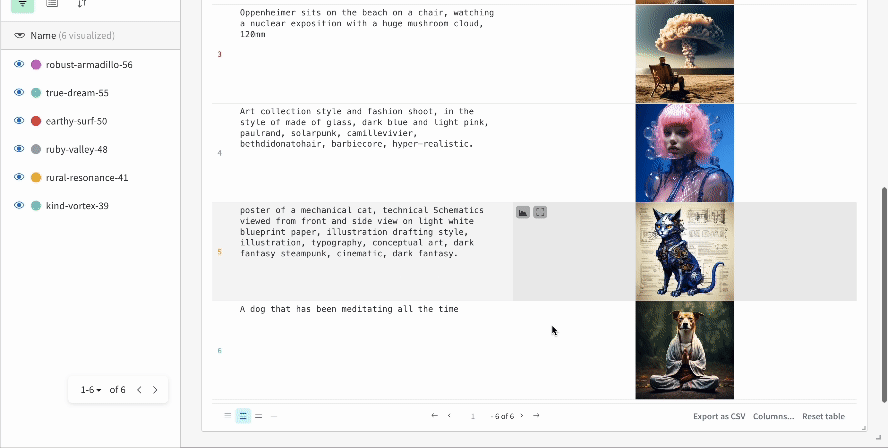 |
|---|
| An example of how the results of multiple experiments are logged in your workspace. |
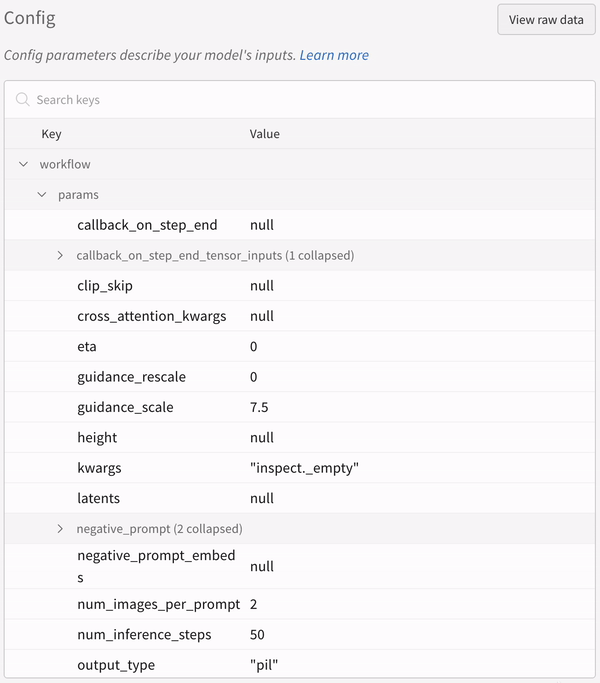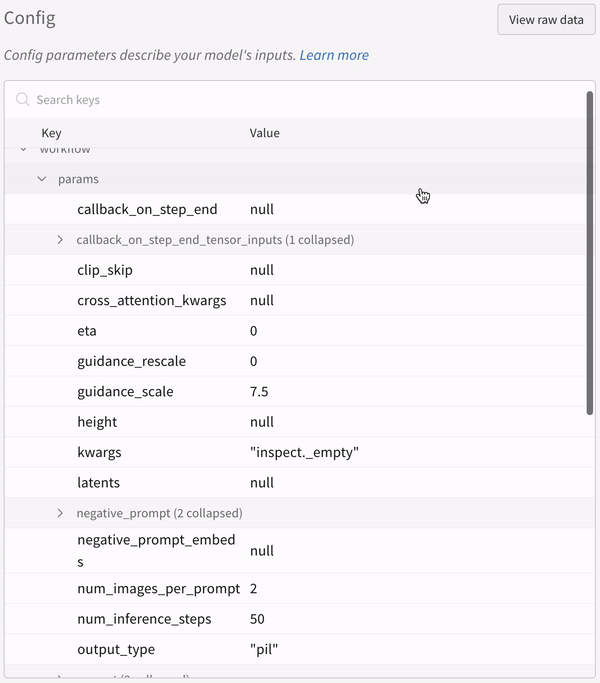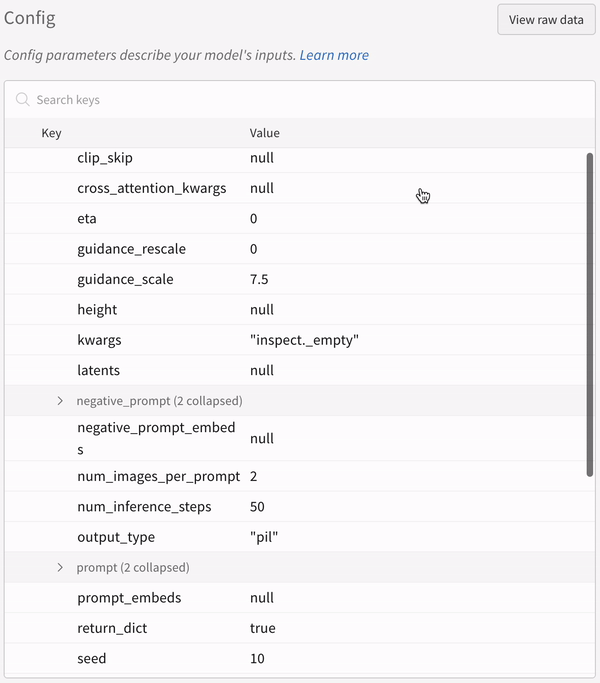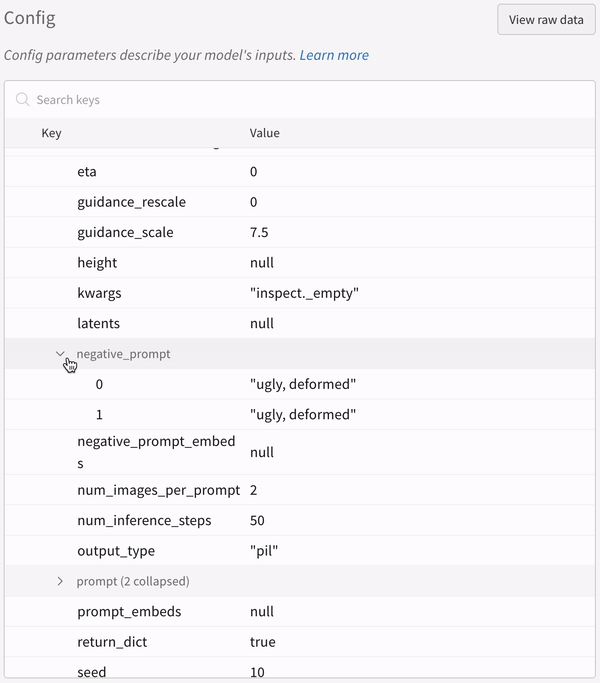 |
|---|
| An example of how the autolog logs the configs of your experiment. |
You need to explicitly call wandb.finish() when executing the code in IPython notebook environments after calling the pipeline. This is not necessary when executing python scripts.
Tracking multi-pipeline workflows
This section demonstrates the autolog with a typical Stable Diffusion XL + Refiner workflow, in which the latents generated by the StableDiffusionXLPipeline is refined by the corresponding refiner.
- Python Script
- Notebook
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline, StableDiffusionXLPipeline
from wandb.integration.diffusers import autolog
# initialize the SDXL base pipeline
base_pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
variant="fp16",
use_safetensors=True,
)
base_pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
# initialize the SDXL refiner pipeline
refiner_pipeline = StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0",
text_encoder_2=base_pipeline.text_encoder_2,
vae=base_pipeline.vae,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
use_safetensors=True,
variant="fp16",
)
refiner_pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
negative_prompt = "static, frame, painting, illustration, sd character, low quality, low resolution, greyscale, monochrome, nose, cropped, lowres, jpeg artifacts, deformed iris, deformed pupils, bad eyes, semi-realistic worst quality, bad lips, deformed mouth, deformed face, deformed fingers, deformed toes standing still, posing"
# Make the experiment reproducible by controlling randomness.
# The seed would be automatically logged to WandB.
seed = 42
generator_base = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(seed)
generator_refiner = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(seed)
# Call WandB Autolog for Diffusers. This would automatically log
# the prompts, generated images, pipeline architecture and all
# associated experiment configs to Weights & Biases, thus making your
# image generation experiments easy to reproduce, share and analyze.
autolog(init=dict(project="sdxl"))
# Call the base pipeline to generate the latents
image = base_pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
output_type="latent",
generator=generator_base,
).images[0]
# Call the refiner pipeline to generate the refined image
image = refiner_pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
image=image[None, :],
generator=generator_refiner
).images[0]
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline, StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import wandb
from wandb.integration.diffusers import autolog
# initialize the SDXL base pipeline
base_pipeline = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
variant="fp16",
use_safetensors=True,
)
base_pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
# initialize the SDXL refiner pipeline
refiner_pipeline = StableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-refiner-1.0",
text_encoder_2=base_pipeline.text_encoder_2,
vae=base_pipeline.vae,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
use_safetensors=True,
variant="fp16",
)
refiner_pipeline.enable_model_cpu_offload()
prompt = "a photo of an astronaut riding a horse on mars"
negative_prompt = "static, frame, painting, illustration, sd character, low quality, low resolution, greyscale, monochrome, nose, cropped, lowres, jpeg artifacts, deformed iris, deformed pupils, bad eyes, semi-realistic worst quality, bad lips, deformed mouth, deformed face, deformed fingers, deformed toes standing still, posing"
# Make the experiment reproducible by controlling randomness.
# The seed would be automatically logged to WandB.
seed = 42
generator_base = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(seed)
generator_refiner = torch.Generator(device="cuda").manual_seed(seed)
# Call WandB Autolog for Diffusers. This would automatically log
# the prompts, generated images, pipeline architecture and all
# associated experiment configs to Weights & Biases, thus making your
# image generation experiments easy to reproduce, share and analyze.
autolog(init=dict(project="sdxl"))
# Call the base pipeline to generate the latents
image = base_pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
output_type="latent",
generator=generator_base,
).images[0]
# Call the refiner pipeline to generate the refined image
image = refiner_pipeline(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
image=image[None, :],
generator=generator_refiner
).images[0]
# Finish the experiment
wandb.finish()
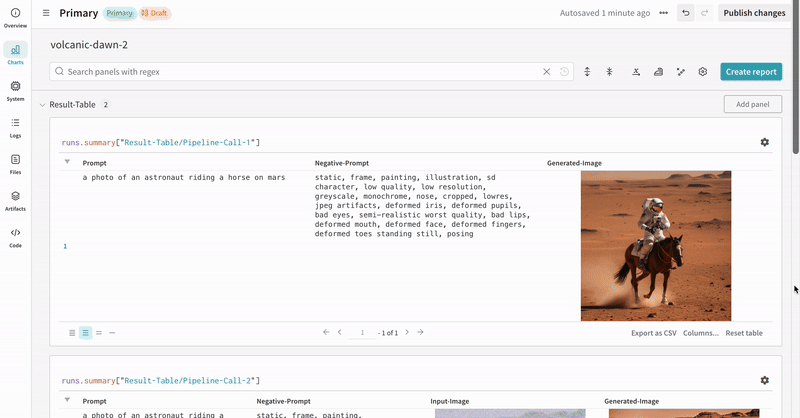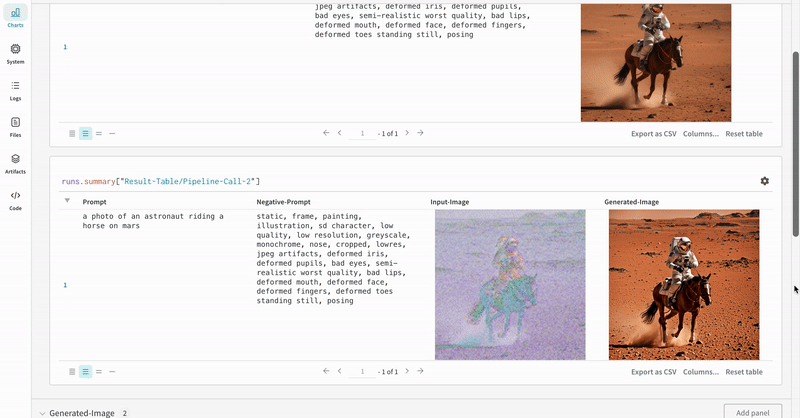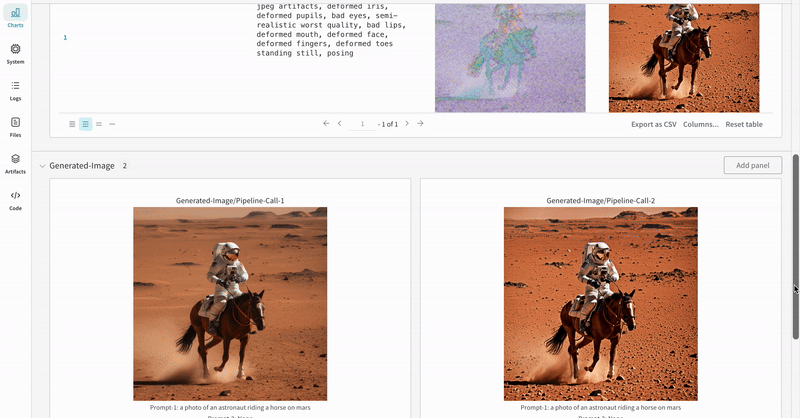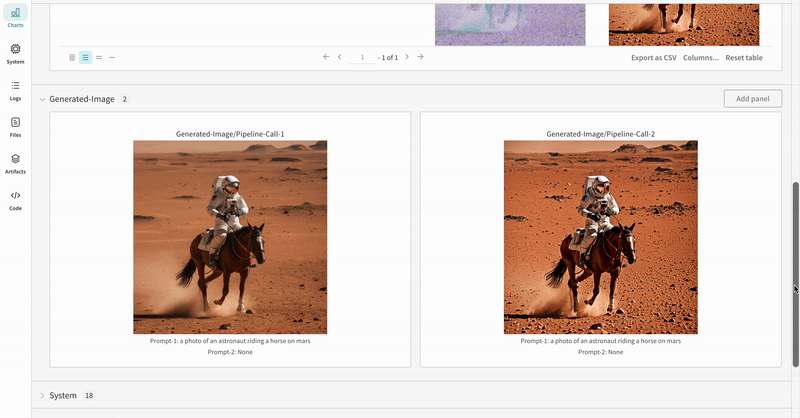 |
|---|
| An example of how the autolog tracks an Stable Diffusion XL + Refiner experiment. |