Walkthrough
The following Quickstart demonstrates how to log data tables, visualize data, and query data.
Select the button below to try a PyTorch Quickstart example project on MNIST data.
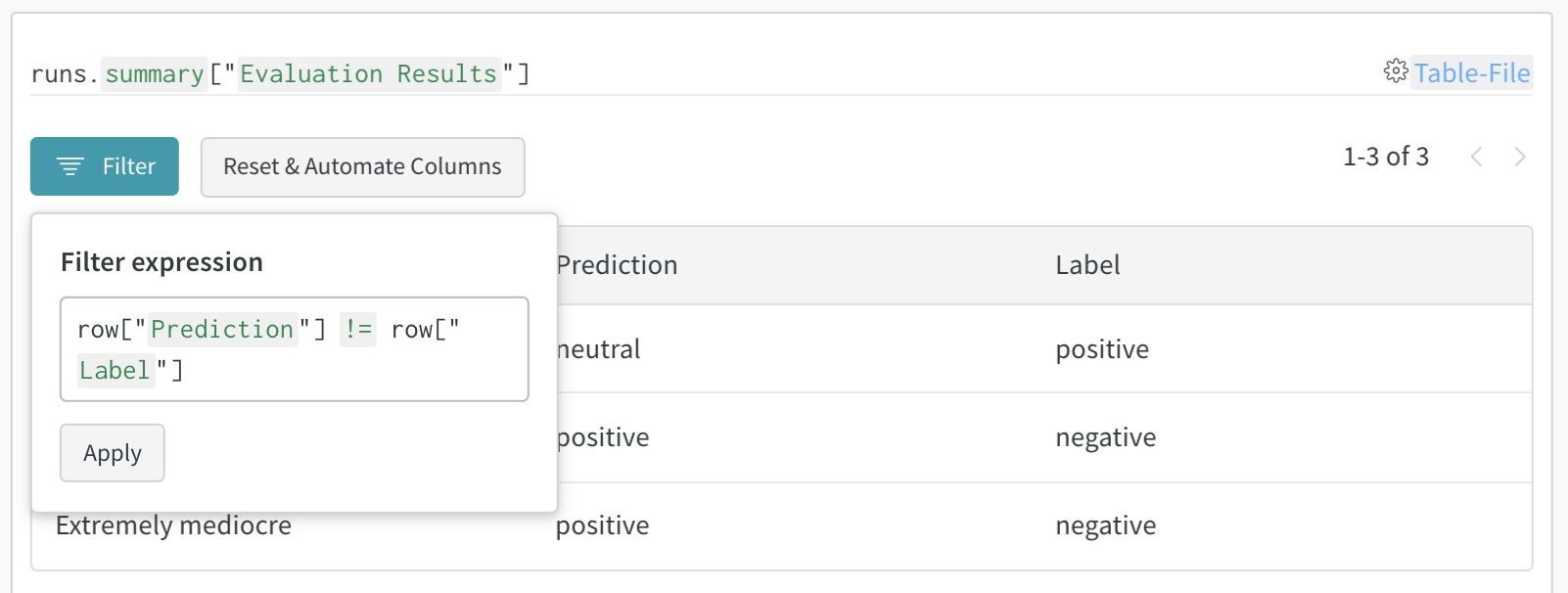
1. Log a table
Log a table with W&B. You can either construct a new table or pass a Pandas DataFrame.
- Construct a table
- Pandas DataFrame
To construct and log a new Table, you will use:
wandb.init(): Create a run to track results.wandb.Table(): Create a new table object.columns: Set the column names.data: Set the contents of each row.
run.log(): Log the table to save it to W&B.
Here's an example:
import wandb
run = wandb.init(project="table-test")
# Create and log a new table.
my_table = wandb.Table(columns=["a", "b"], data=[["a1", "b1"], ["a2", "b2"]])
run.log({"Table Name": my_table})
Pass a Pandas DataFrame to wandb.Table() to create a new table.
import wandb
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("my_data.csv")
run = wandb.init(project="df-table")
my_table = wandb.Table(dataframe=df)
wandb.log({"Table Name": my_table})
For more information on supported data types, see the wandb.Table in the W&B API Reference Guide.
2. Visualize tables in your project workspace
View the resulting table in your workspace.
- Navigate to your project in the W&B App.
- Select the name of your run in your project workspace. A new panel is added for each unique table key.
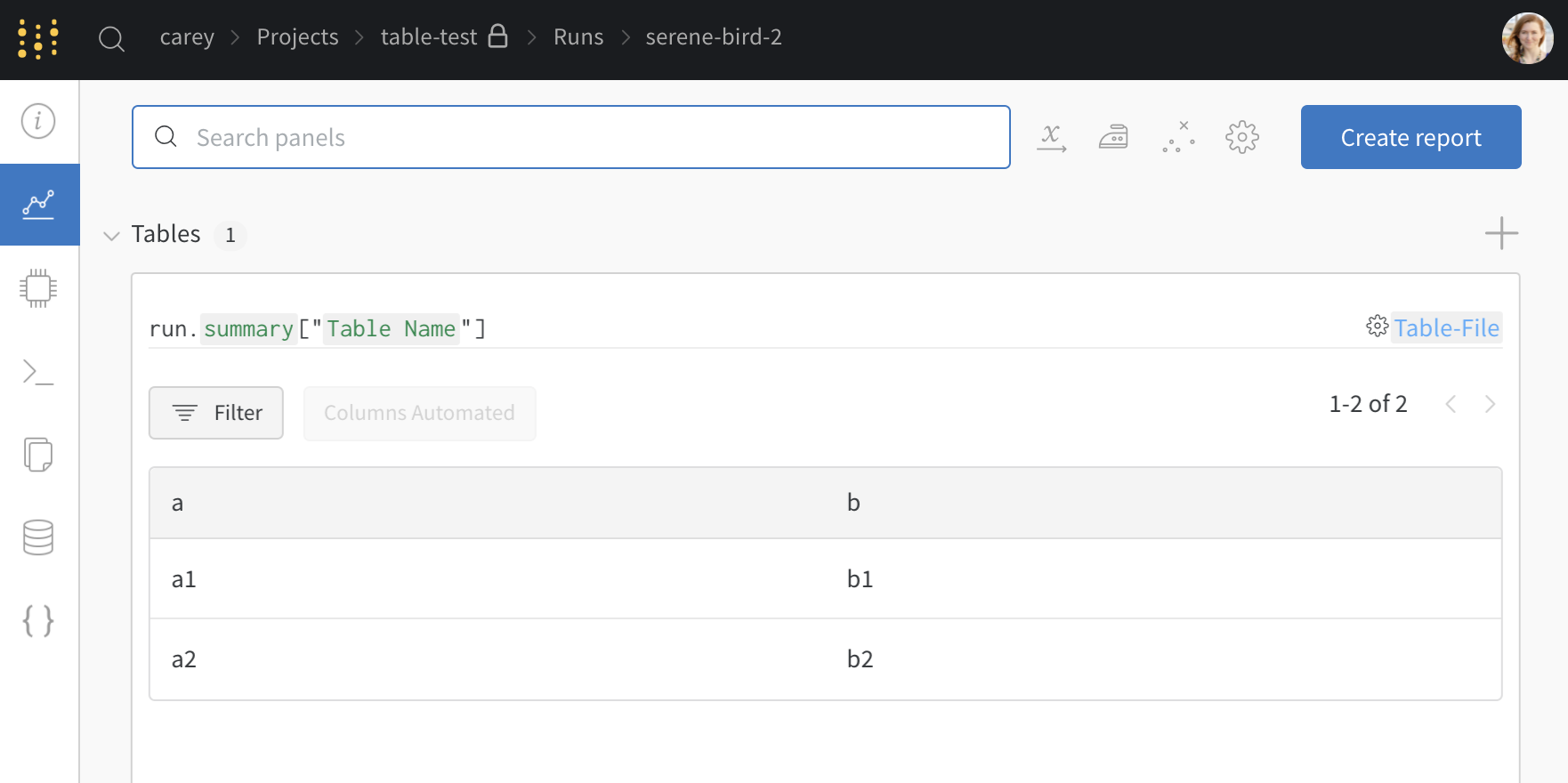
In this example, my_table, is logged under the key "Table Name".
3. Compare across model versions
Log sample tables from multiple W&B Runs and compare results in the project workspace. In this example workspace, we show how to combine rows from multiple different versions in the same table.
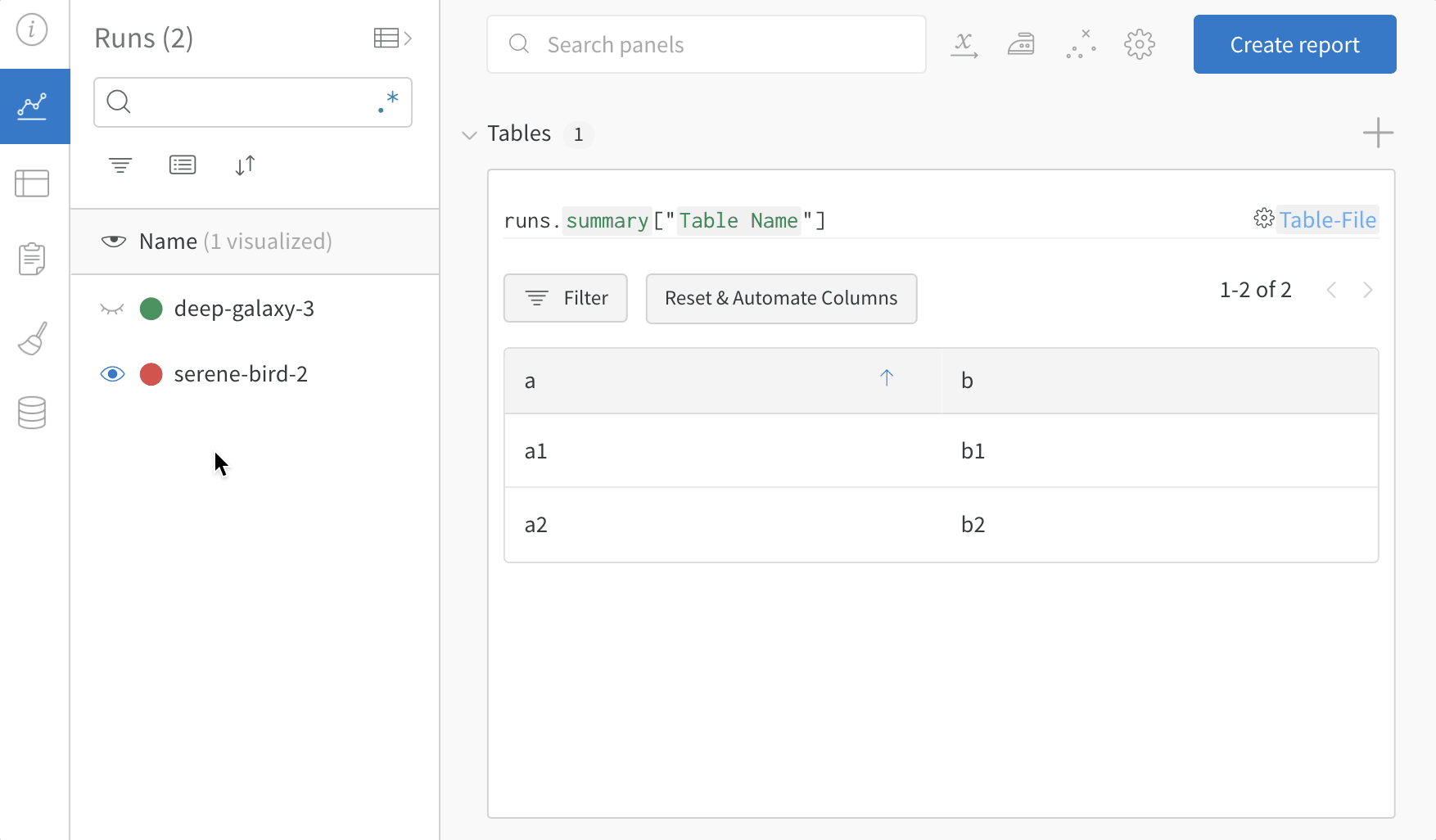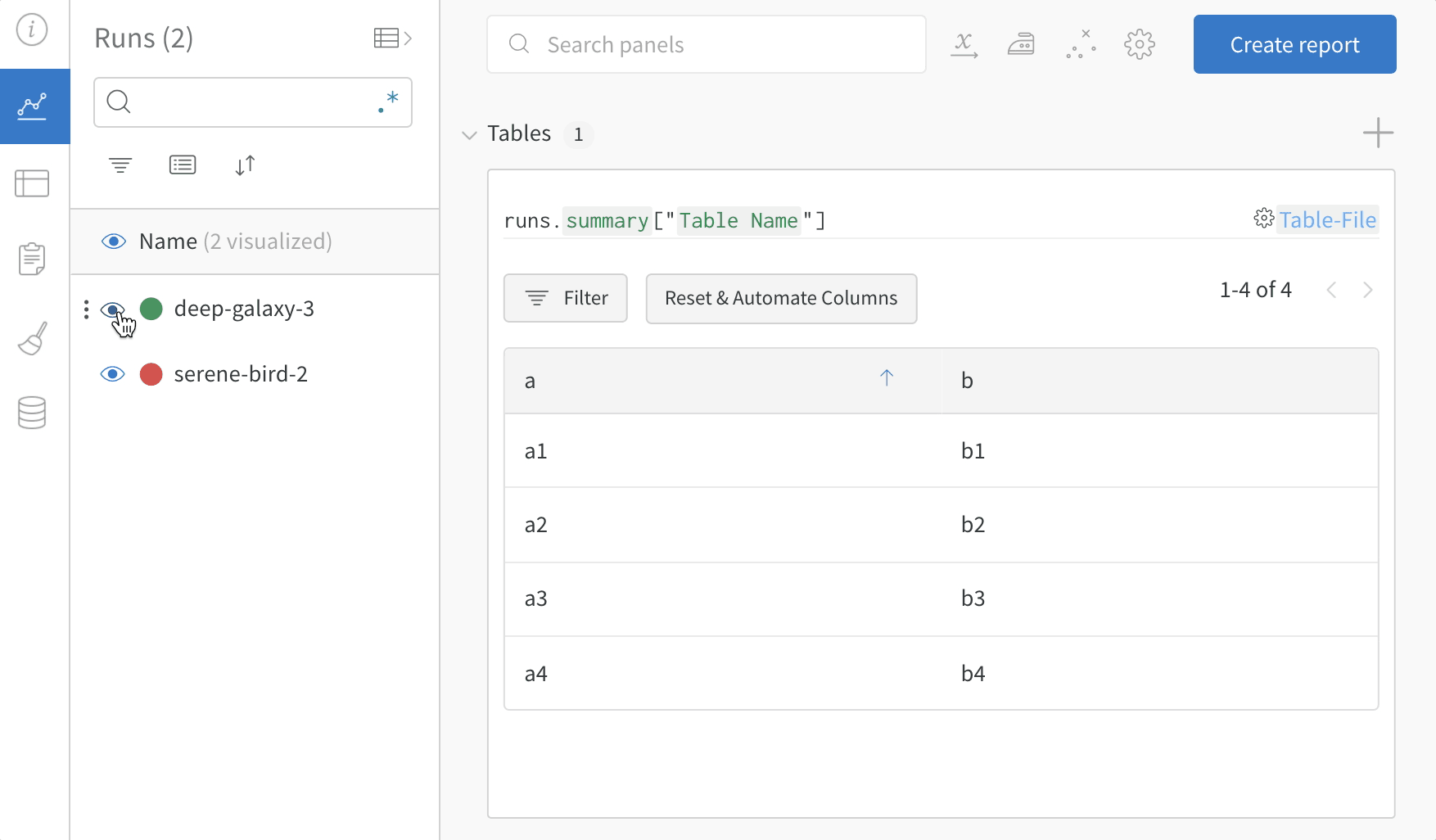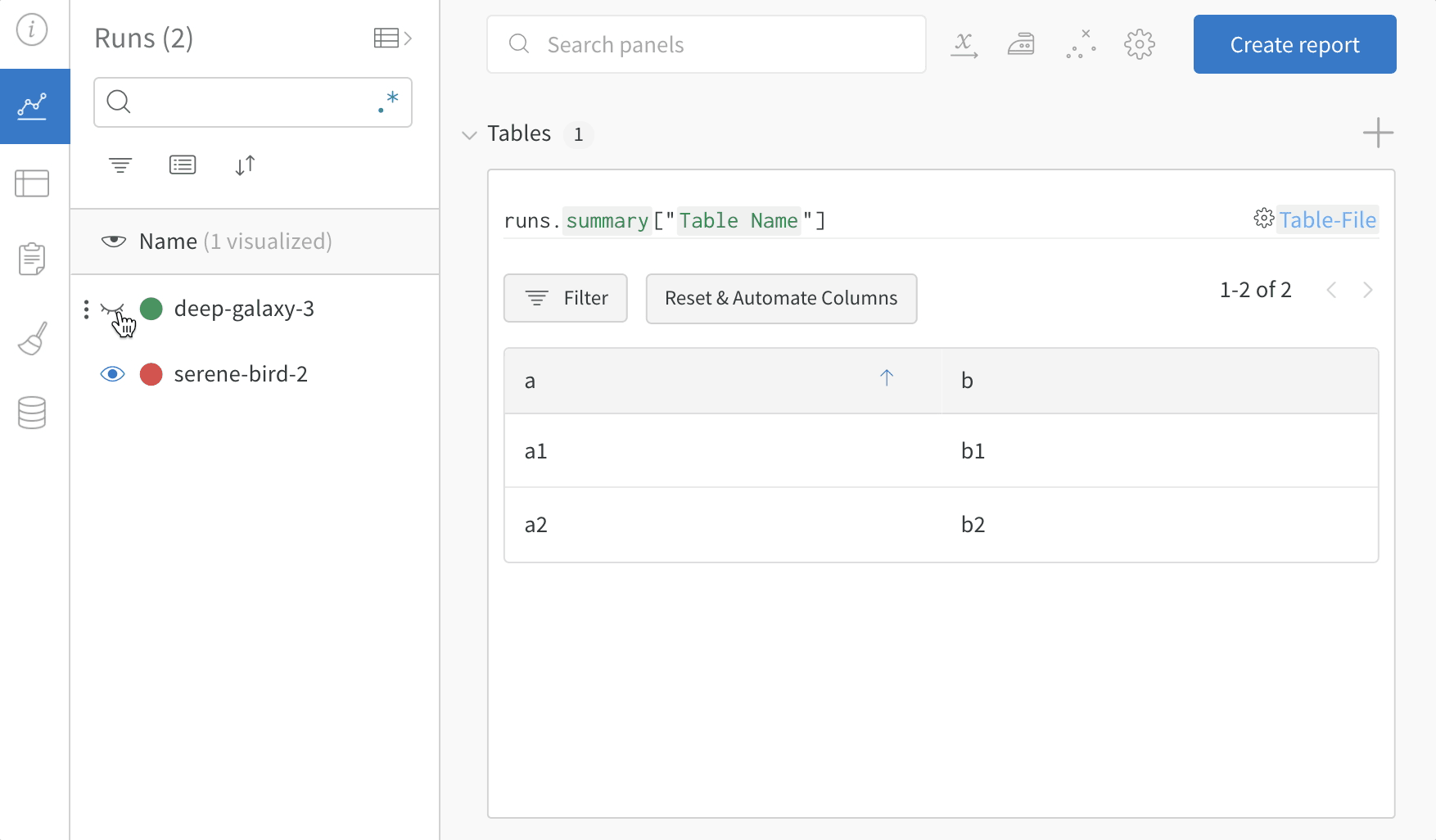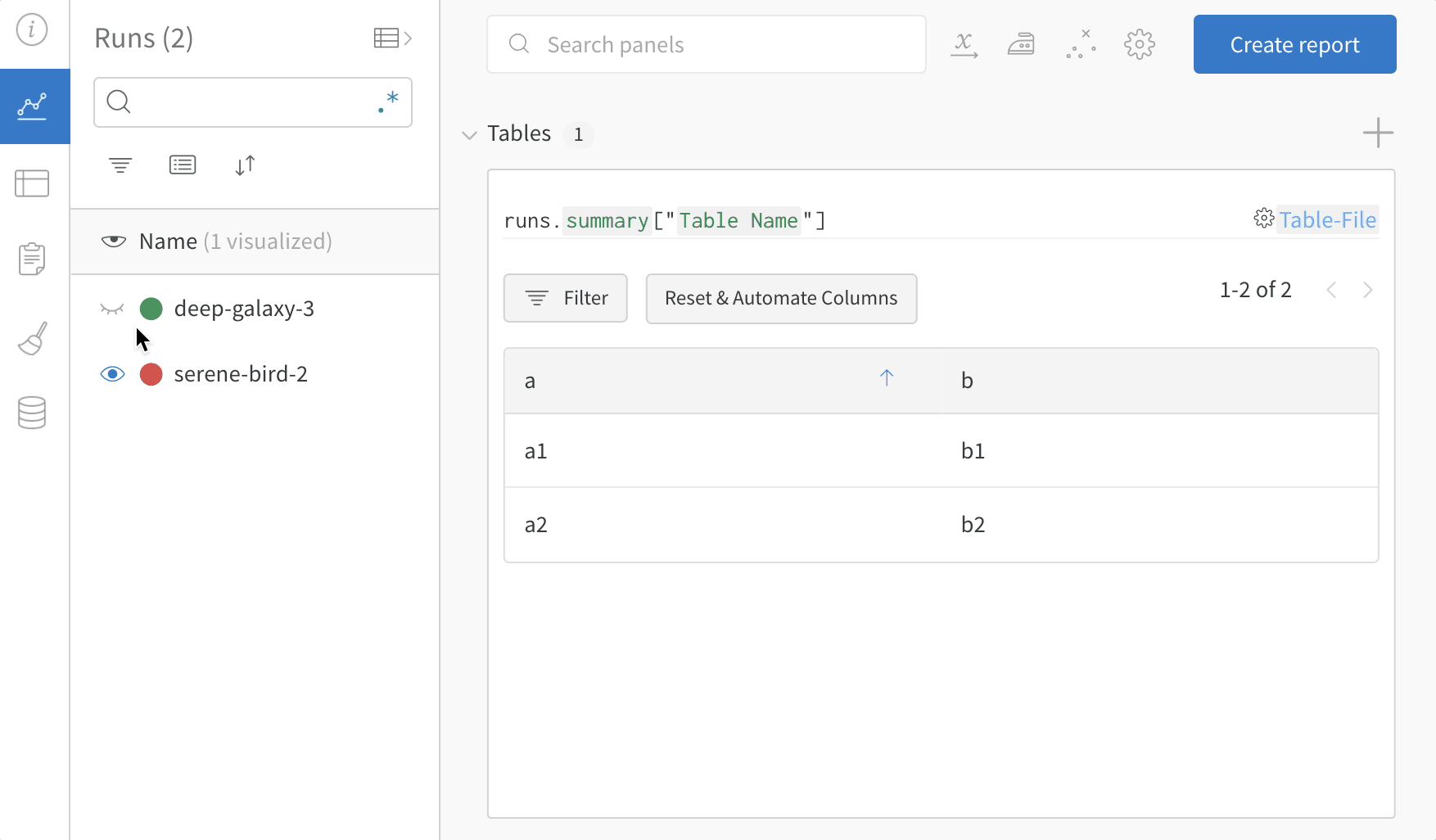
Use the table filter, sort, and grouping features to explore and evaluate model results.